Time: 2021-04-22Views: 200
The direct cause of the temperature rise of the PCB board is due to the existence of circuit power consumption devices, which are generally caused by the following factors:
1. The device selection is unreasonable, and the gas power consumption is too large;
2. The heat sink is not installed, resulting in abnormal heat conduction;
3. The PCB is locally unreasonable, causing local or global temperature rise;
4. PCB design, wiring and heat dissipation design is unreasonable, causing heat concentration.
In view of common heat dissipation factors, we propose some common solutions for this factor when PCB design and thermal design are planned:
1. Device selection
When selecting a model, the device with low power consumption is preferred under the premise that the same function can be realized. Of course, this is also from some considerations in cost.
2. Device layout
Before the layout, we should start with the heat dissipation modules from the schematic diagram, such as the common PMU modules, DCDC modules and some unit main control chips with relatively large heat dissipation, as shown in Figure 1. In the layout, we generally place these large heat-dissipating modules in blocks, and separate the non-severe heat-dissipating modules with a distance of 3-5mm.
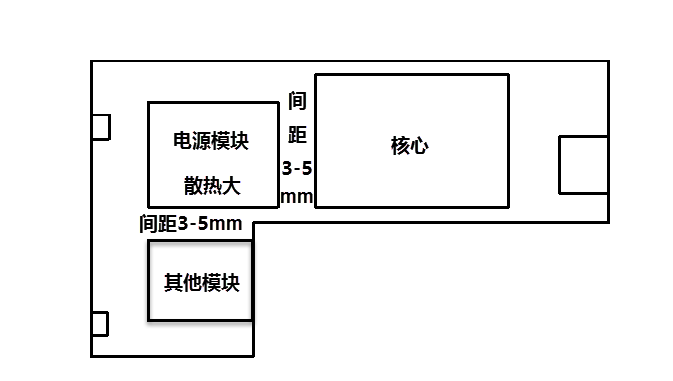
Figure 1 Distribution of PCB heat dissipation layout
At the same time, if conditions permit, heat sinks can be added to the main control chip with severe heat dissipation, as shown in Figure 2.
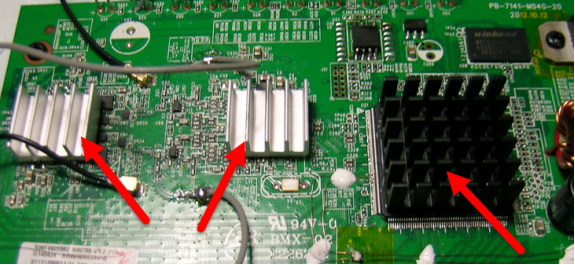
Figure 2 Increase the heat sink to enhance the heat dissipation method
3. Treatment of heat dissipation of PCB wiring
Good PCB copper wiring is also an important way to strengthen heat dissipation:
1) Add windowed vias to the heat dissipation pad of the chip, as shown in Figure 3, allowing the heat dissipated by the chip to be introduced into a large area of the same surface to disperse heat through the vias on the heat dissipation pad to achieve the purpose of heat dissipation.
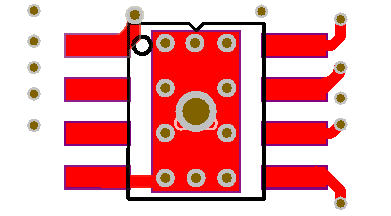
Figure 3 Adding a windowed via on the thermal pad
2) On the basis of drilling holes on the heat dissipation pad, we can increase the heat dissipation area as much as possible. We can add copper leakage on the front and back impedance layers at the same time, and add heat dissipation vias at the same time. As shown in Figure 4
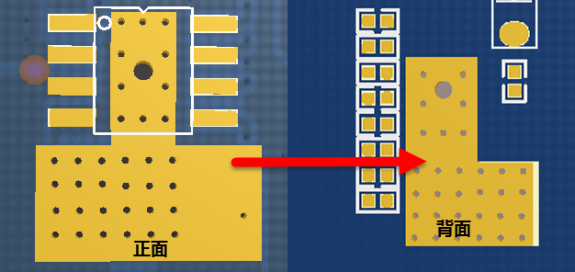
Figure 4 Open windows on the front and back to increase the heat dissipation area
The analysis of the above factors from the PCB is an effective way to solve the temperature rise of the printed board. These factors are often related and dependent on each other in a product and system. Most of the factors should be analyzed according to the actual situation, and only for a specific The actual situation can solve the problem more correctly and reduce the temperature rise.
